Background of the School of Science and Engineering
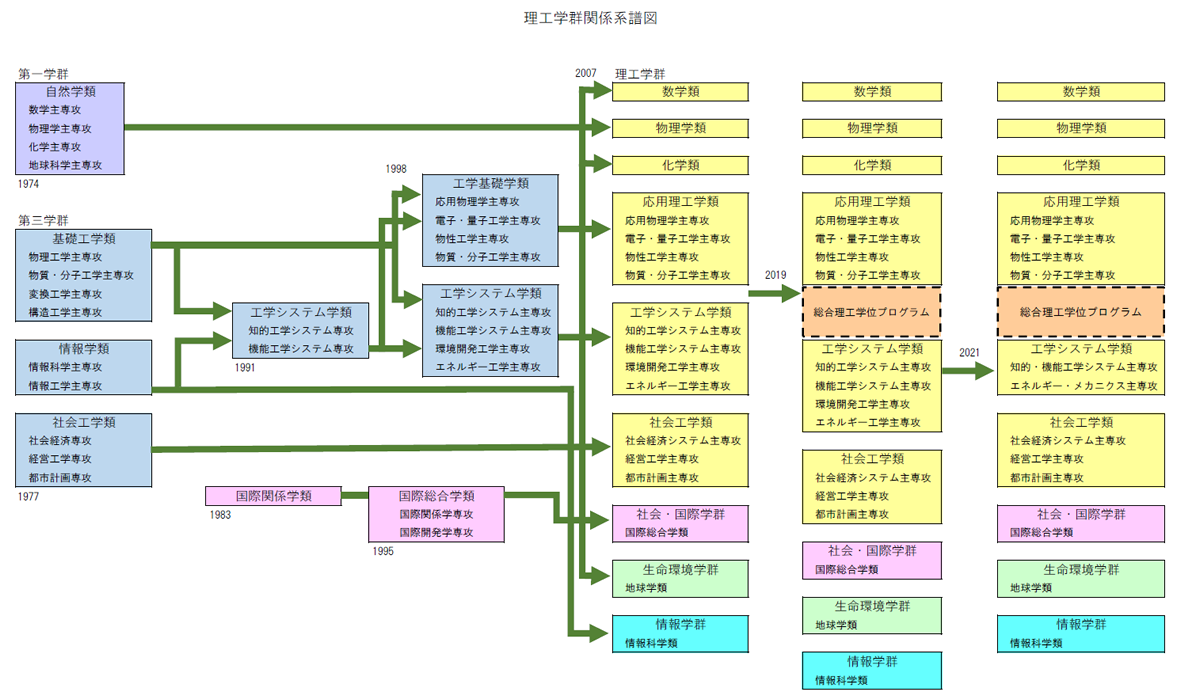
The University of Tsukuba’s School of Science and Engineering was established in April 2007 as an educational organization focused on the fundamentals and applications of natural science. The University of Tsukuba itself was founded in 1973 as a university comprising departments carried over from the former Tokyo University of Education, as well as newly established departments. Since then, education at the schools of the University of Tsukuba has been characterized by a First Cluster of Colleges (pure), Second Cluster of Colleges (biology, human beings), and Third Cluster of Colleges (applications, international). Under this system, humanities and science divisions are established in each field. However, the schools were reorganized in April 2007 to make the organization and school names easier to understand for the general public. The School of Science and Engineering was launched as an educational organization encompassing the fields of science and engineering.
Also, in October 2019, a Bachelor’s Program in Interdisciplinary Engineering (for foreign students studying in Japan) was established enabling students to acquire a bachelor’s degree based only on classes in English.
History of the Science Field
The forerunner of the three colleges which make up the science field of the School of Science and Engineering (College of Mathematics, College of Physics, College of Chemistry) was the College of Natural Sciences, First Cluster of Colleges, which was established by splitting off the biology field from the Faculty of Science of the Tokyo University of Education when the University of Tsukuba was established in October 1973. In the College of Natural Sciences, four majors were established: mathematics, physics, chemistry, and geoscience. With the reorganization in April 2007, the Geoscience Major became the College of Geoscience, School of Life and Environmental Sciences, and the Mathematics Major, Physics Major, and Chemistry Major became, respectively, today’s College of Mathematics, College of Physics, and College of Chemistry in the School of Science and Engineering.
History of the Engineering Field
The Third Cluster of Colleges, the forerunner of the engineering field in the School of Science and Engineering, was already established in 1977 with three colleges: College of Policy and Planning Sciences, College of Information Sciences, and College of Engineering Sciences. Later, the College of International Relations was launched in 1983, and the College of Engineering Systems in 1991, resulting in five colleges. In 1995, an International Development Major was added to the College of International Relations, and it became the College of International Studies. In 1998, the College of Engineering Systems changed to four majors. In 2007, the university established the School of Science and Engineering, comprising three science colleges—the College of Mathematics, College of Physics, and College of Chemistry—and three engineering colleges—the College of Engineering Sciences, College of Engineering Systems, and College of Policy and Planning Sciences.
Then, in October 2019, a Bachelor’s Program in Interdisciplinary Engineering (for foreign students studying in Japan) was established enabling students to acquire a bachelor’s degree based only on classes in English.
In the 2021 academic year, the four majors of the College of Engineering Systems were reduced to two majors.
Chronology of the School of Science and Engineering
|
Year
|
School of Science and Engineering
|
Science Schools and Colleges
|
Engineering Schools and Colleges
|
|---|---|---|---|
| October 1973 | Establishment of the University of Tsukuba College of Natural Sciences, First Cluster of Colleges Mathematics Major Physics Major Chemistry Major Geoscience Major |
||
| April 1974 | Admission of first class of the College of Natural Sciences, First Cluster of Colleges | ||
| 1977 | Establishment of Third Cluster of Colleges College of Policy and Planning Sciences College of Information Sciences College of Engineering Sciences |
||
| 1983 | Established College of International Relations | ||
| 1991 | Established College of Engineering Systems | ||
| 1995 | College of International Studies (Added International Development Major due to reorganization of College of International Relations) |
||
| 1998 | College of Engineering Sciences (Reorganized into College of Engineering Sciences with four majors, and College of Engineering Systems with four majors) |
||
| 2007 | Establishment of School of Science and Engineering | ||
| College of Mathematics | Transferred from the majors of the previous College of Natural Sciences, First Cluster of Colleges (The Geoscience Major of the College of Natural Sciences became the College of Geoscience, School of Life and Environmental Sciences) |
||
| College of Physics | |||
| College of Chemistry | |||
| College of Engineering Sciences | Transferred from the previous Third Cluster of Colleges (The College of Information Engineering became the College of Information Science and the College of Media Arts, Science and Technology of the School of Informatics, while the College of International Relations became the School of Social and International Studies) |
||
| College of Engineering Systems | |||
| College of Policy and Planning Sciences | |||
| 2019 | Established Bachelor’s Program in Interdisciplinary Engineering | ||
Past Deans and Associate Deans
|
Year
|
Dean
|
Assistant Dean
|
|---|---|---|
| 2007.4-2008.3 | OKAMOTO Kenichi (Chemistry) | YOSHIDA Masatoshi (Policy and Planning Sciences) |
| 2008.4-2010.3 | YOSHIDA Masatoshi (Policy and Planning Sciences) | TAKEUCHI Mitsuhiro (Mathematics) |
| 2010.4-2012.3 | KITA Eiji (Engineering Sciences) | MASUMOTO Yasuaki (Physics) |
| 2012.4-2014.3 | YASUNOBU Seiji (Engineering Systems) | SAITO Kazuya (Chemistry) |
| 2014.4-2016.3 | MIYAMOTO Masahiko (Mathematics) | ITOIGAWA Eiichi (Policy and Planning Sciences) |
| 2016.4-2018.3 | SANO Nobuyuki (Engineering Sciences) | HATSUGAI Yasuhiro (Physics) |
| 2018.4-2020.3 | NISHIOKA Makihito (Engineering Systems) | MORIHASHI Kenji (Chemistry) |
| 2020.4-2022.3 | AKIYAMA Eizo (Policy and Planning Sciences) | AKIYAMA Shigeki (Mathematics) |
| 2022.4-2024.3 | UKEGAWA Fumihiko (Physics) | HINO Ken-ichi (Engineering Sciences) |


 Japanese
Japanese